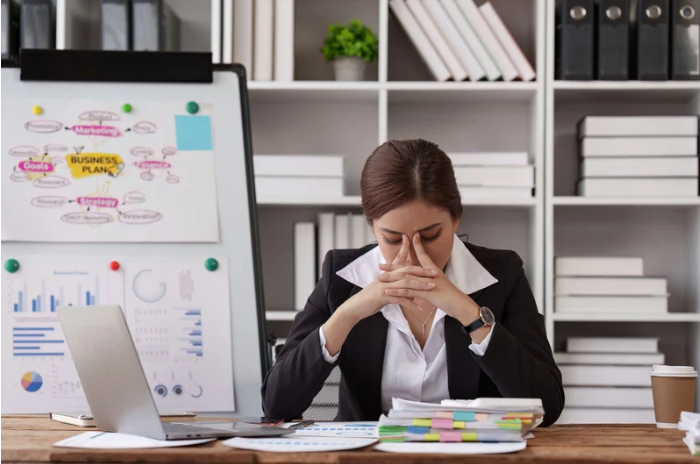
In today’s fast-paced business world, stress is an unavoidable reality. While short-term stress can be a motivating factor, chronic stress negatively impacts productivity, decision-making, and overall business performance. By understanding the neuroscience behind stress and its effects on the brain, business leaders can implement strategies to create a healthier work environment and optimize performance.
The Impact of Cortisol on Productivity and Problem-Solving
Cortisol, commonly known as the stress hormone, plays a crucial role in the body’s fight-or-flight response. When faced with pressure, the brain releases cortisol to help improve alertness and energy. However, prolonged exposure to high cortisol levels can have detrimental effects on cognitive function, including:
- Impaired Decision-Making: Chronic stress shifts brain activity from the prefrontal cortex (responsible for rational thinking) to the amygdala (associated with emotional responses). This leads to impulsive, reactionary decision-making rather than strategic problem-solving.
- Reduced Focus and Productivity: Excess cortisol disrupts neural pathways involved in memory and concentration, making it harder to stay focused on tasks and prioritize effectively.
- Decreased Creativity: Stress narrows cognitive flexibility, limiting the ability to think outside the box and innovate in business scenarios.
Neuroscience-Backed Ways to Manage Stress in High-Pressure Environments
Managing stress effectively requires a combination of neuroscience-backed strategies that support brain health and resilience:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Studies show that mindfulness practices reduce cortisol levels and enhance activity in the prefrontal cortex, improving emotional regulation and decision-making.
- Physical Activity: Exercise releases endorphins, which counteract the effects of cortisol and improve overall brain function.
- Controlled Breathing Techniques: Practices like deep breathing and box breathing activate the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing stress responses and restoring cognitive balance.
- Adequate Sleep: Sleep deprivation exacerbates stress, while quality sleep enhances cognitive function, emotional regulation, and problem-solving abilities.
- Nutrition for Brain Health: A diet rich in omega-3s, antioxidants, and vitamins supports brain function and reduces inflammation linked to chronic stress.
How Leaders Can Create a Mentally Healthy Workplace
Business leaders play a critical role in shaping workplace culture and reducing stress among employees. Some key strategies include:
- Encouraging Work-Life Balance: Promoting flexible work arrangements, reasonable deadlines, and breaks helps employees manage stress effectively.
- Fostering Psychological Safety: Creating an environment where employees feel comfortable expressing concerns without fear of retribution encourages open communication and trust.
- Implementing Stress-Reduction Programs: Offering workshops on mindfulness, stress management, and resilience training equips employees with tools to handle workplace challenges.
- Leading by Example: When leaders prioritize their mental well-being, employees are more likely to adopt healthy stress-management habits.
Conclusion
Stress is an inevitable part of business, but unmanaged stress can lead to poor decision-making, reduced productivity, and a toxic work culture. By understanding the neuroscience of stress and implementing practical strategies, business leaders can create environments that support resilience, innovation, and long-term success. Investing in mental well-being is not just a personal priority – it’s a business imperative.